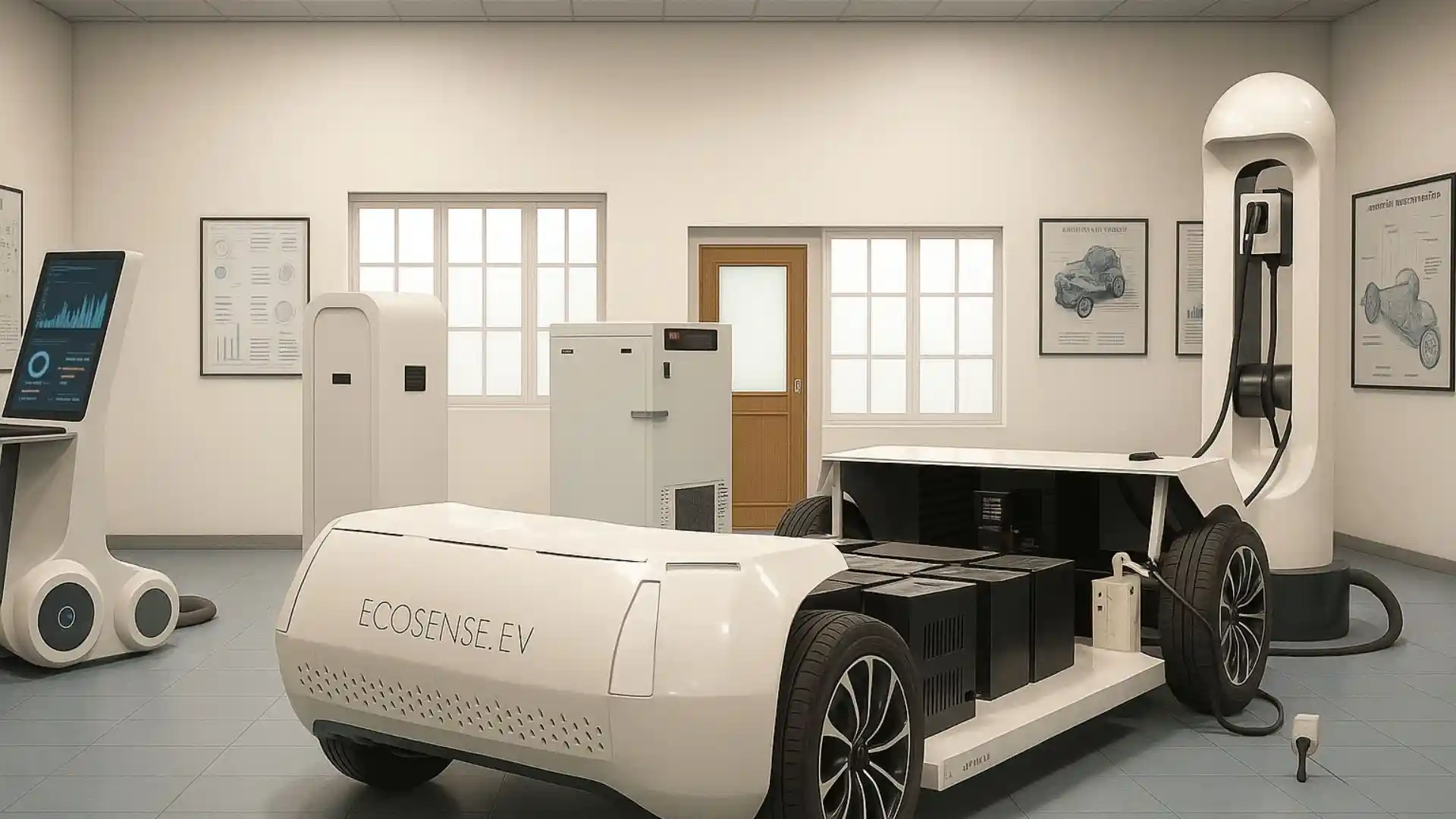
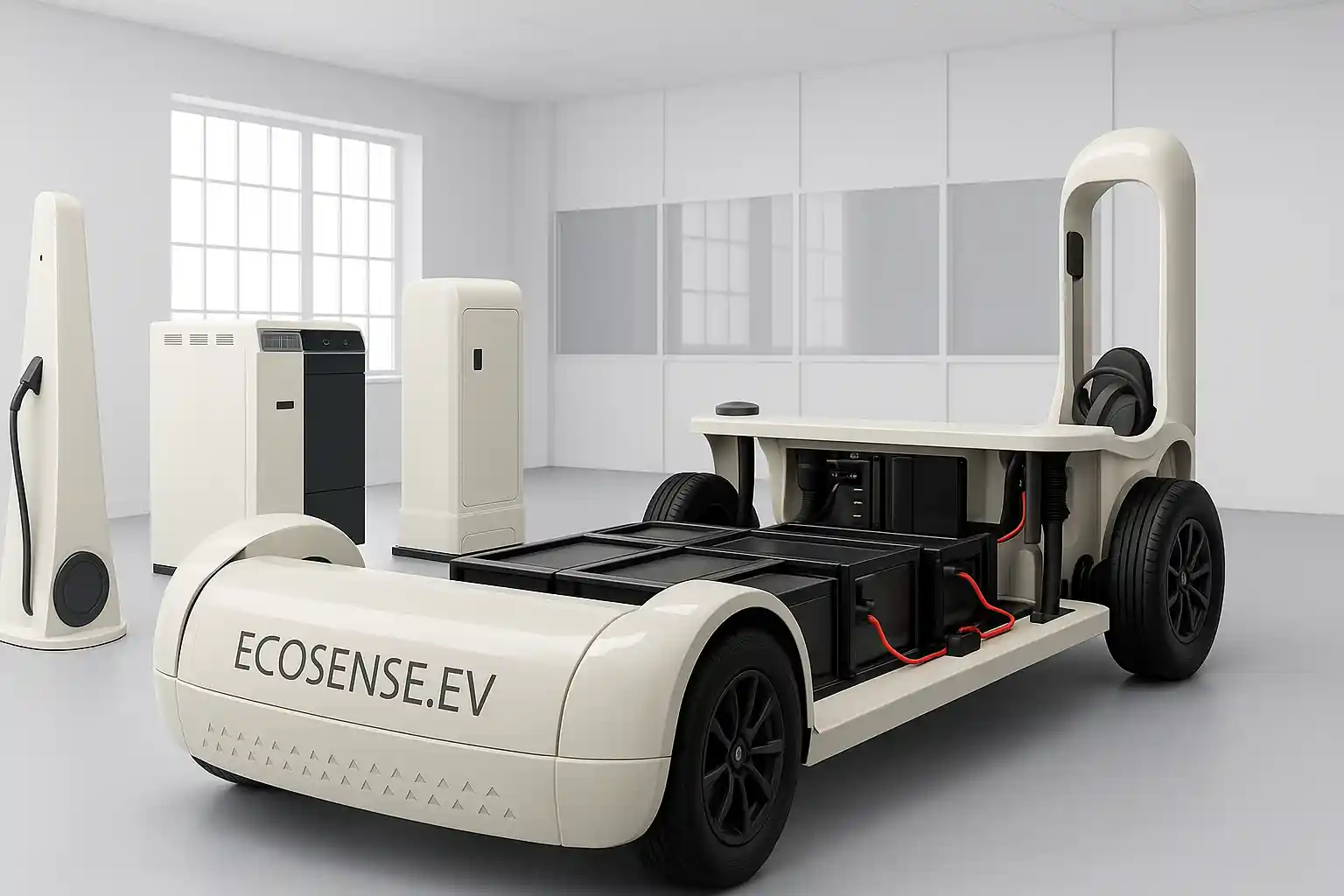
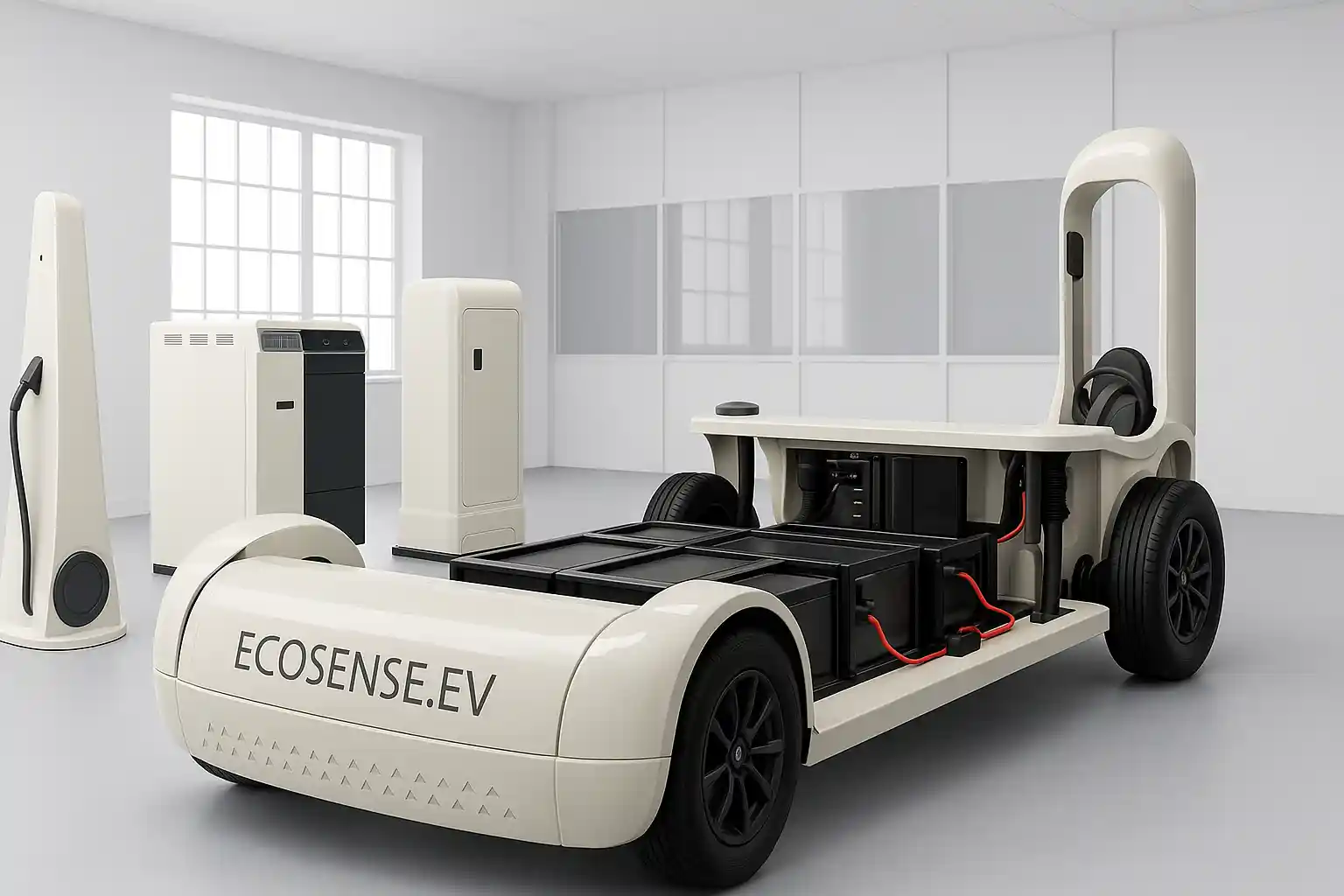
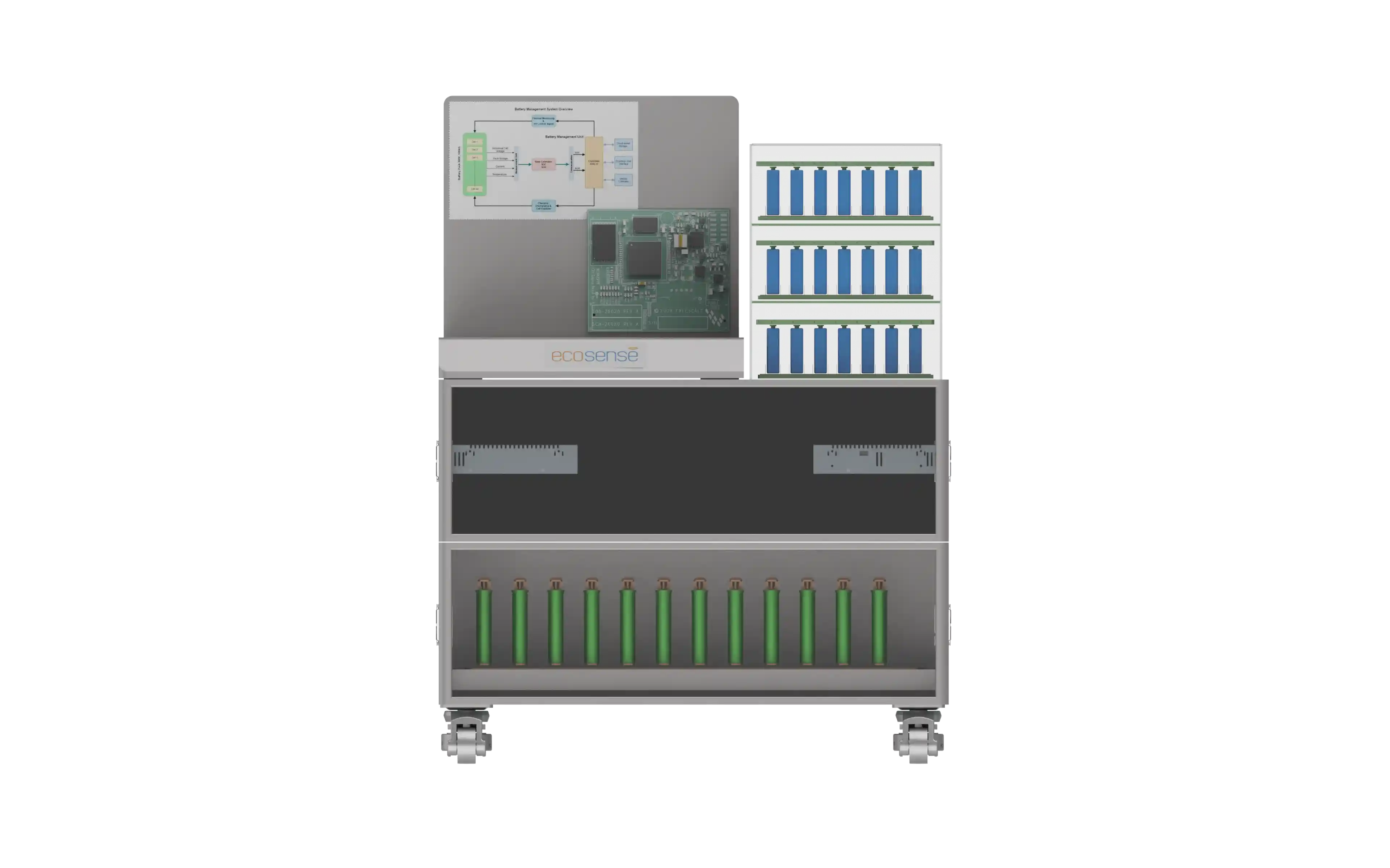
EV Drive Line Simulator with Controller Development & Validation Platform
The EV Driveline Simulator with Controller Development & Validation Platform is a complete hardware-integrated environment designed for mastering electric vehicle propulsion systems. It enables students, researchers, and engineers to design, test, and validate motor control algorithms on real PMSM traction motors, interact with a programmable dynamometer, execute drive cycles, and evaluate full charging–discharging workflows. The platform replicates a true EV energy ecosystem—from grid to battery to motor and back—making it ideal for advanced learning, research, and prototype development in electric mobility.