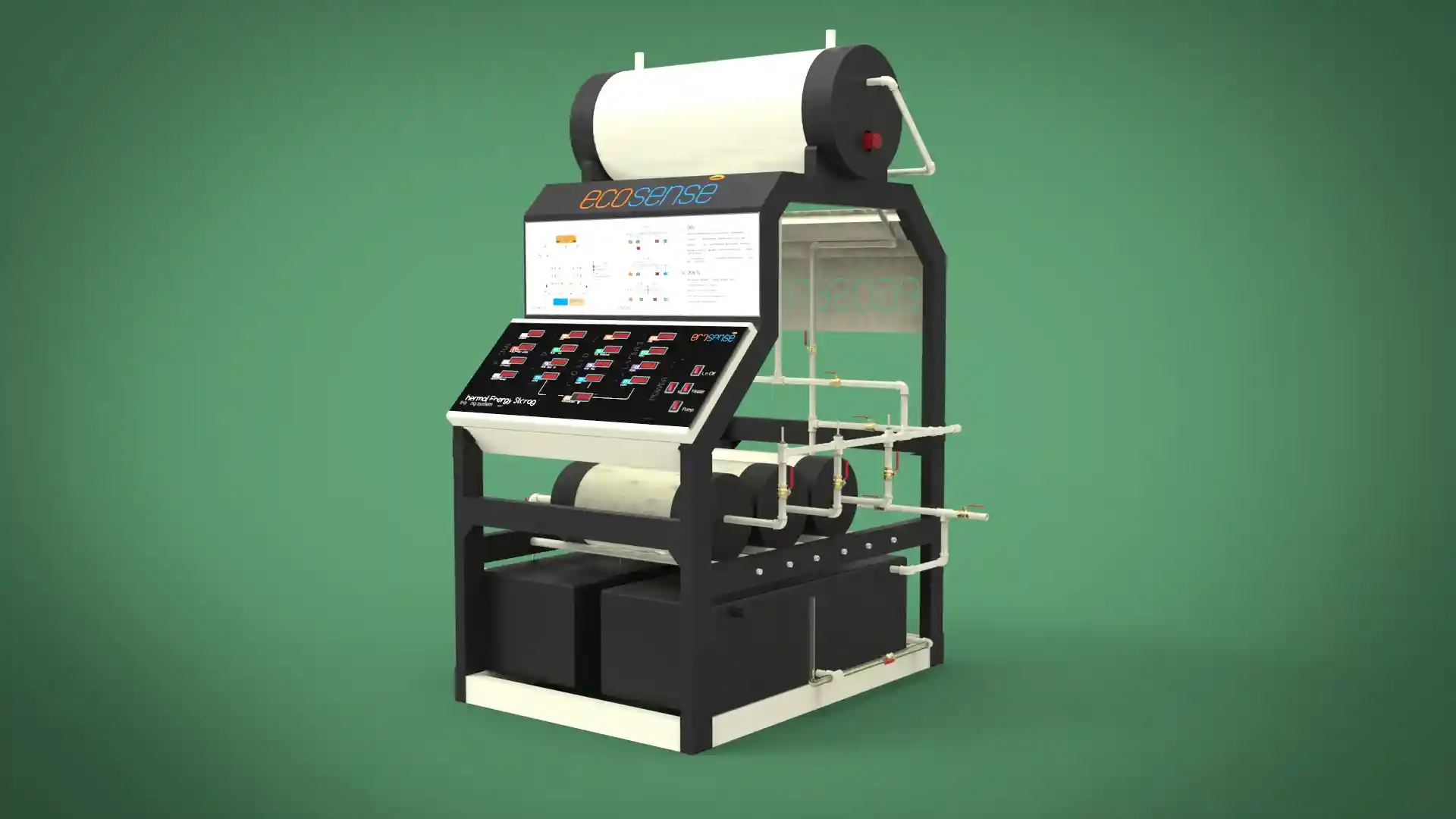
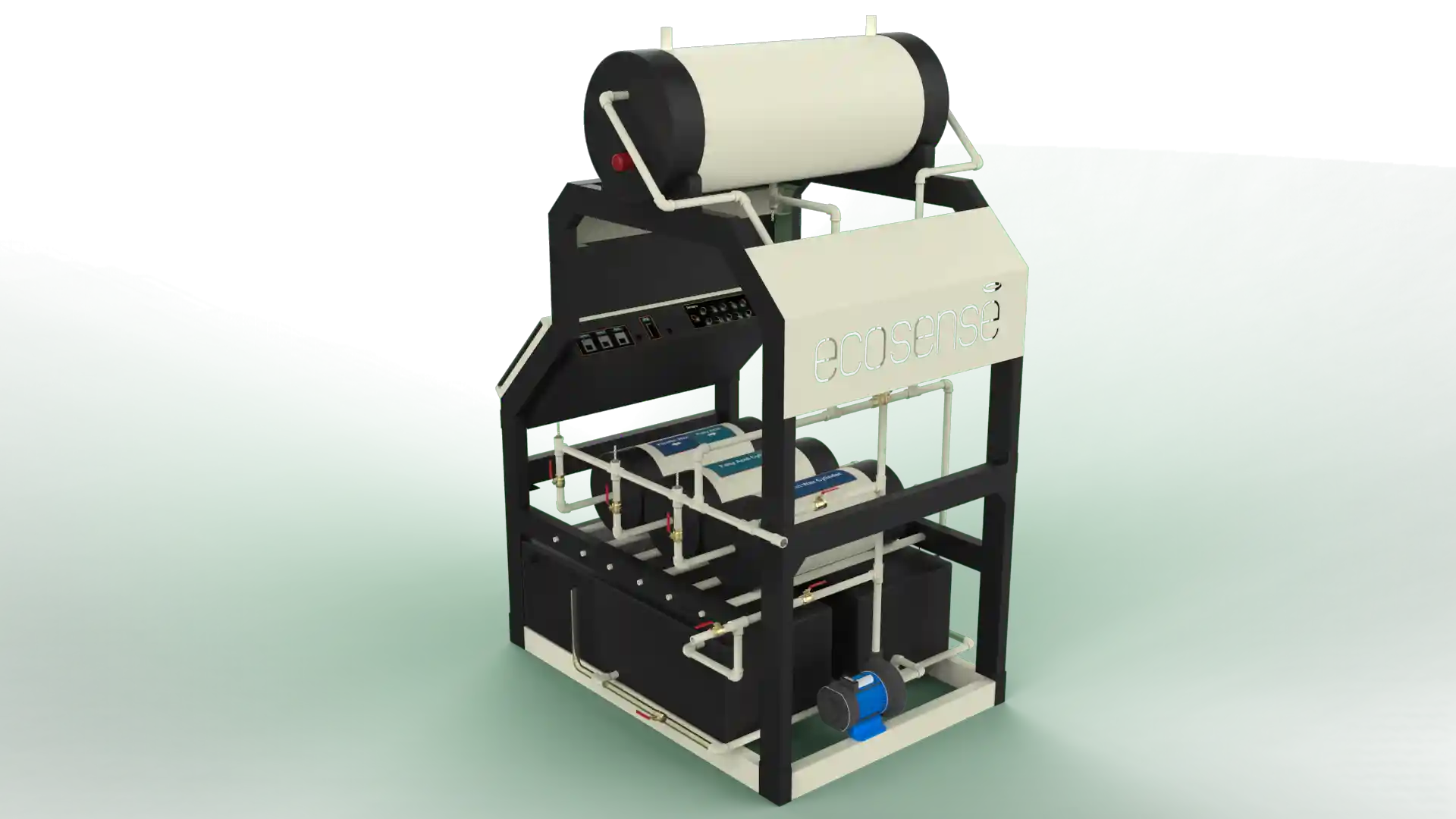
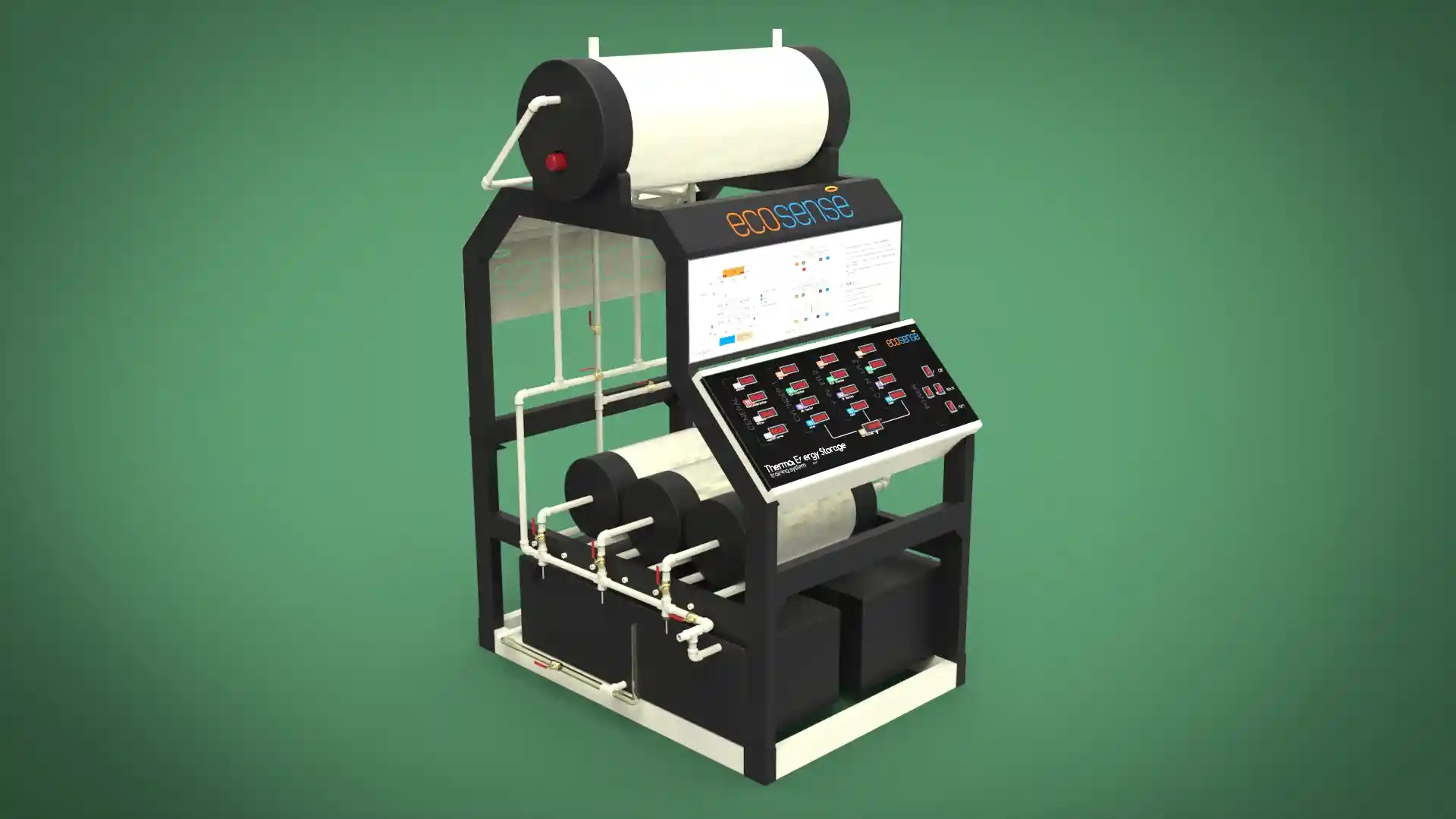
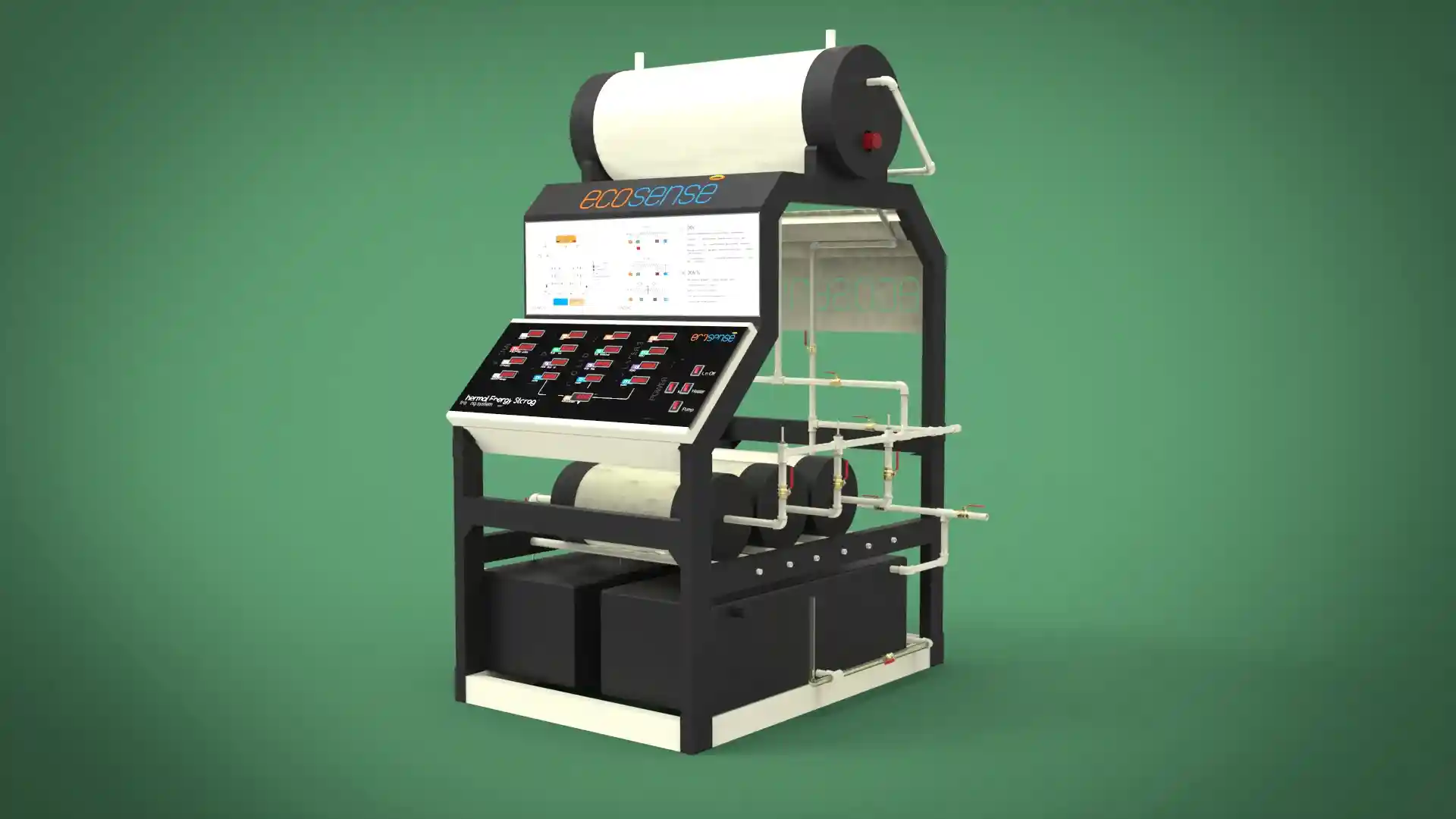
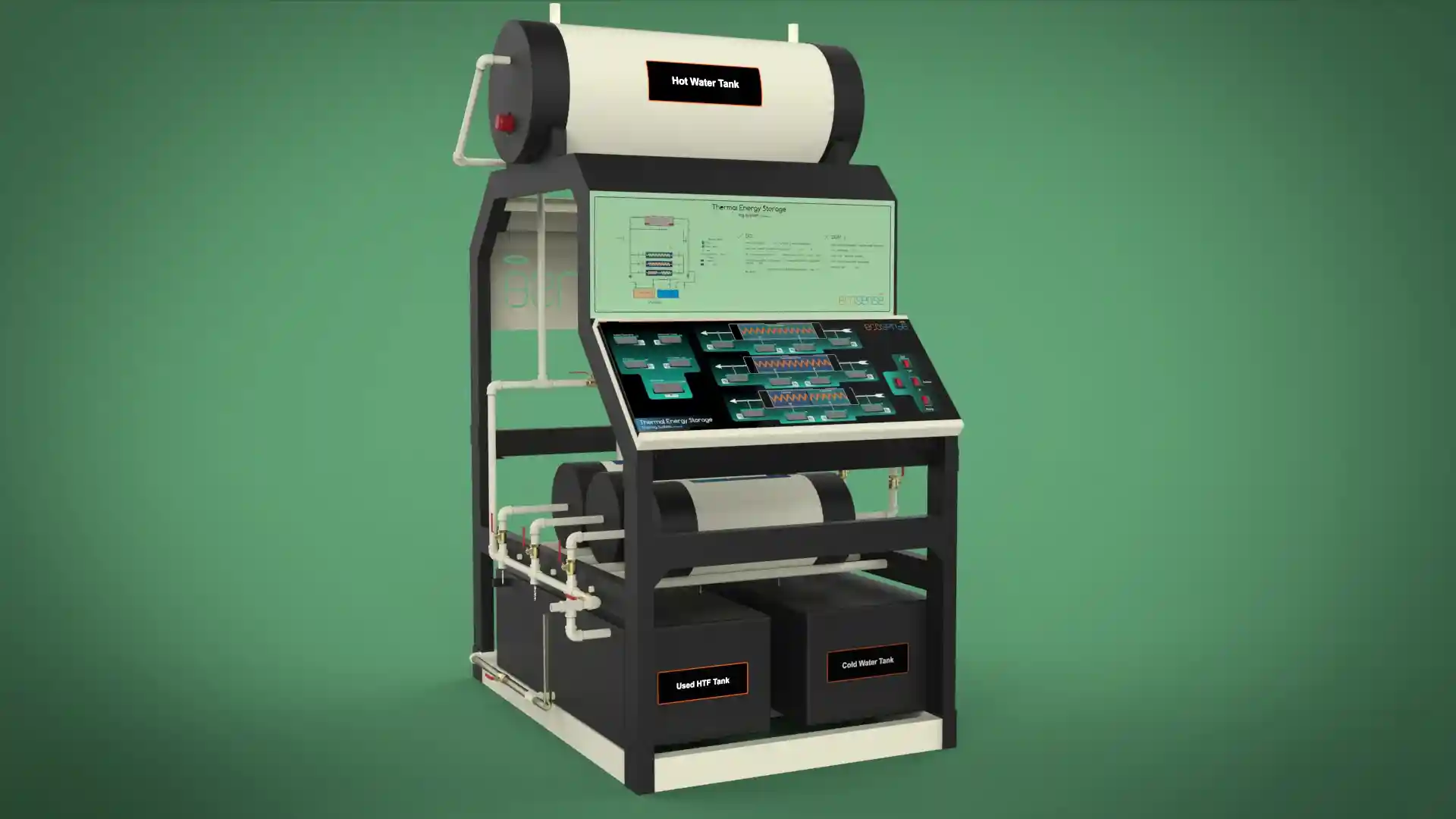
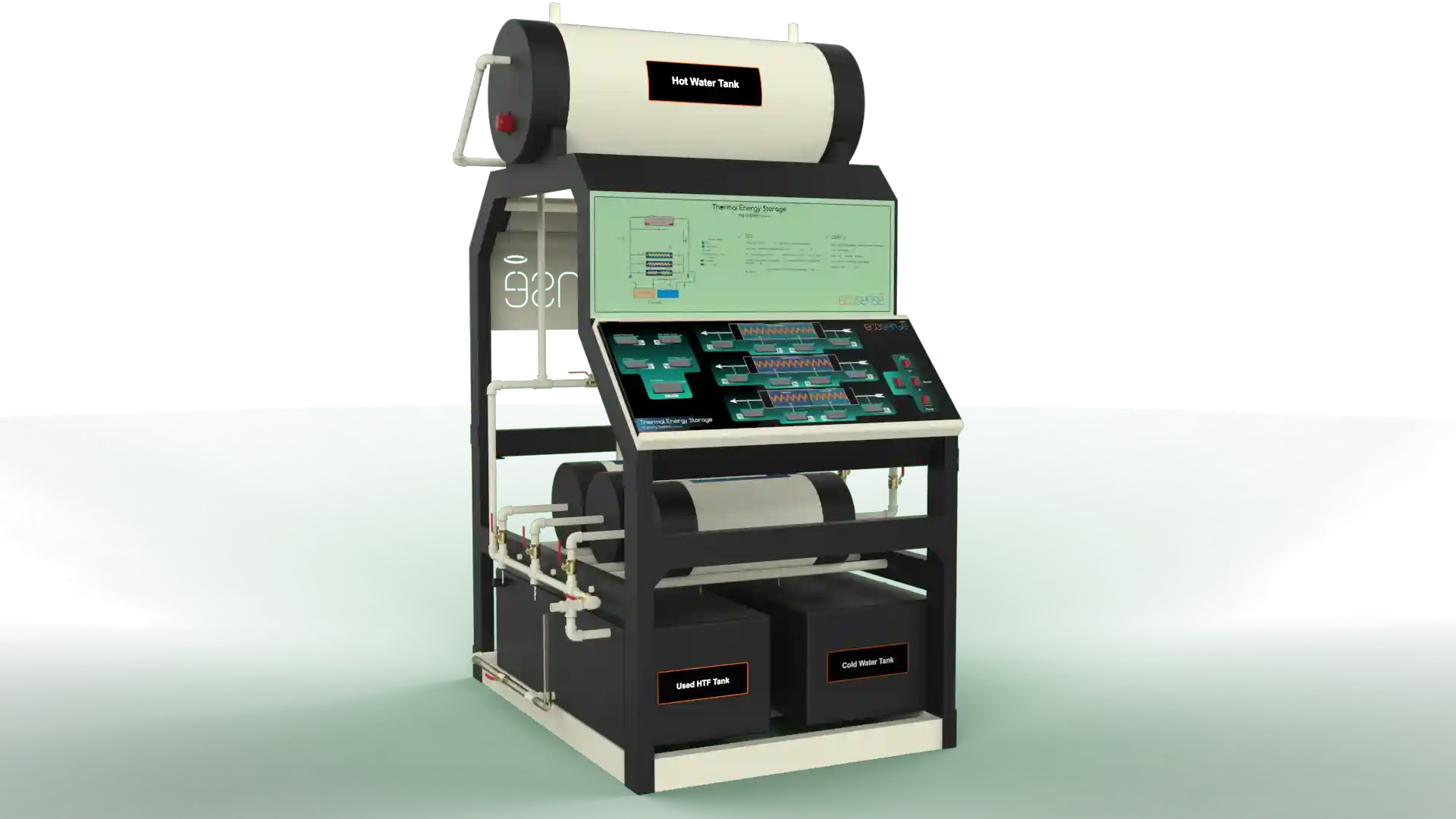
Thermal Energy Storage System
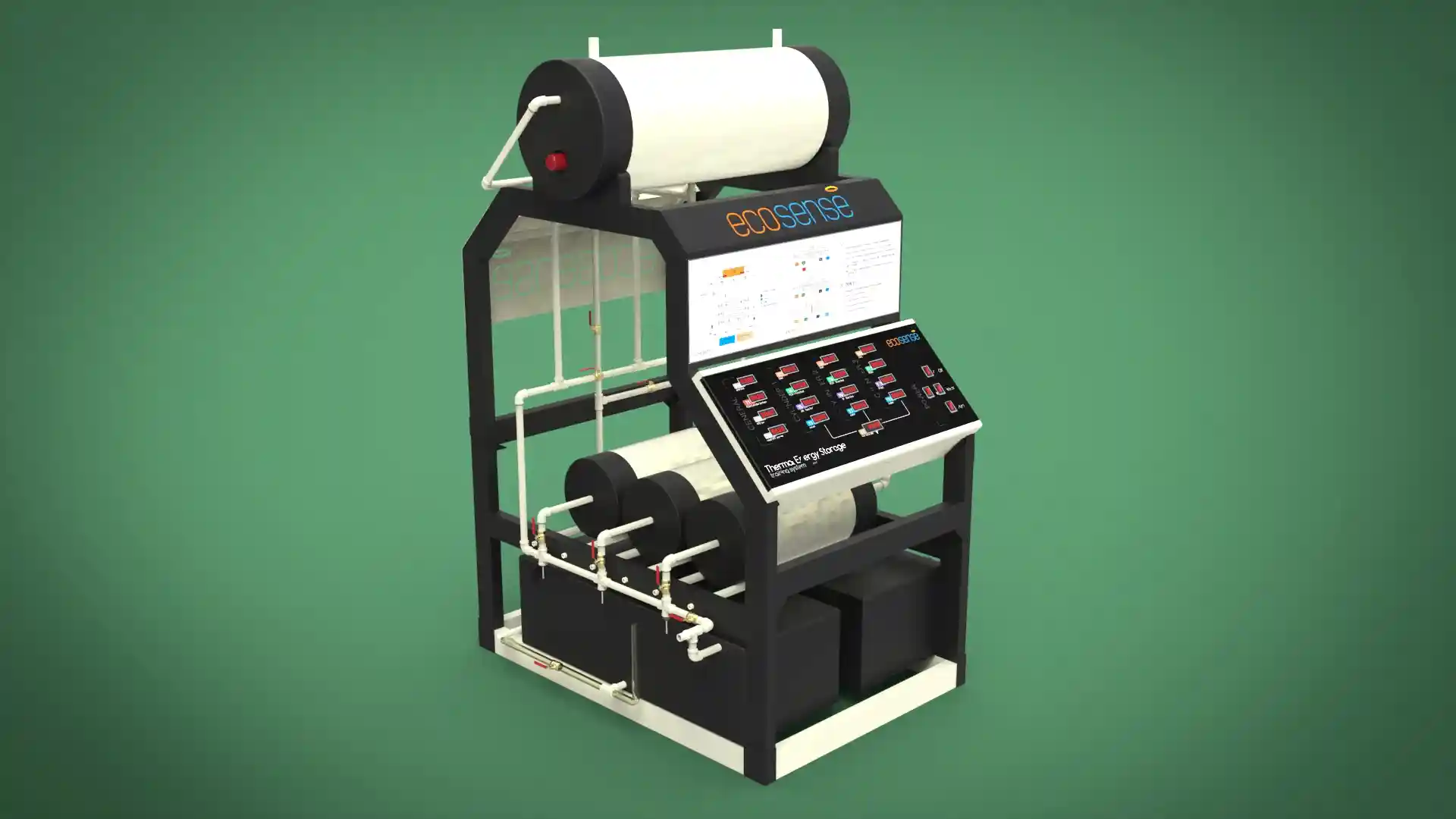
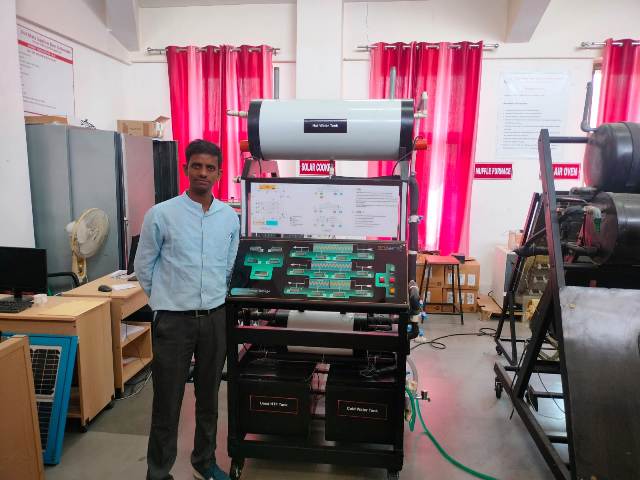
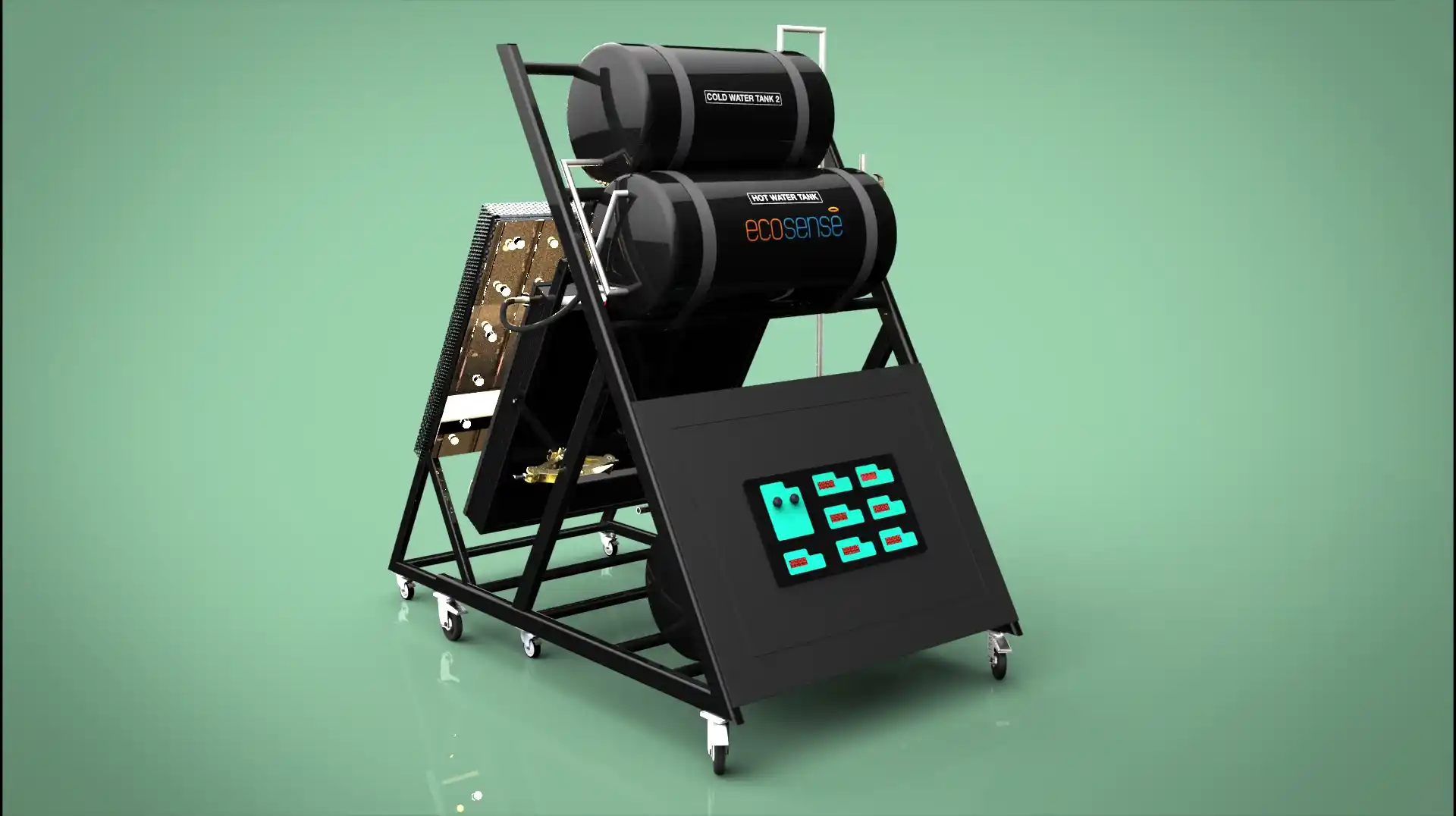
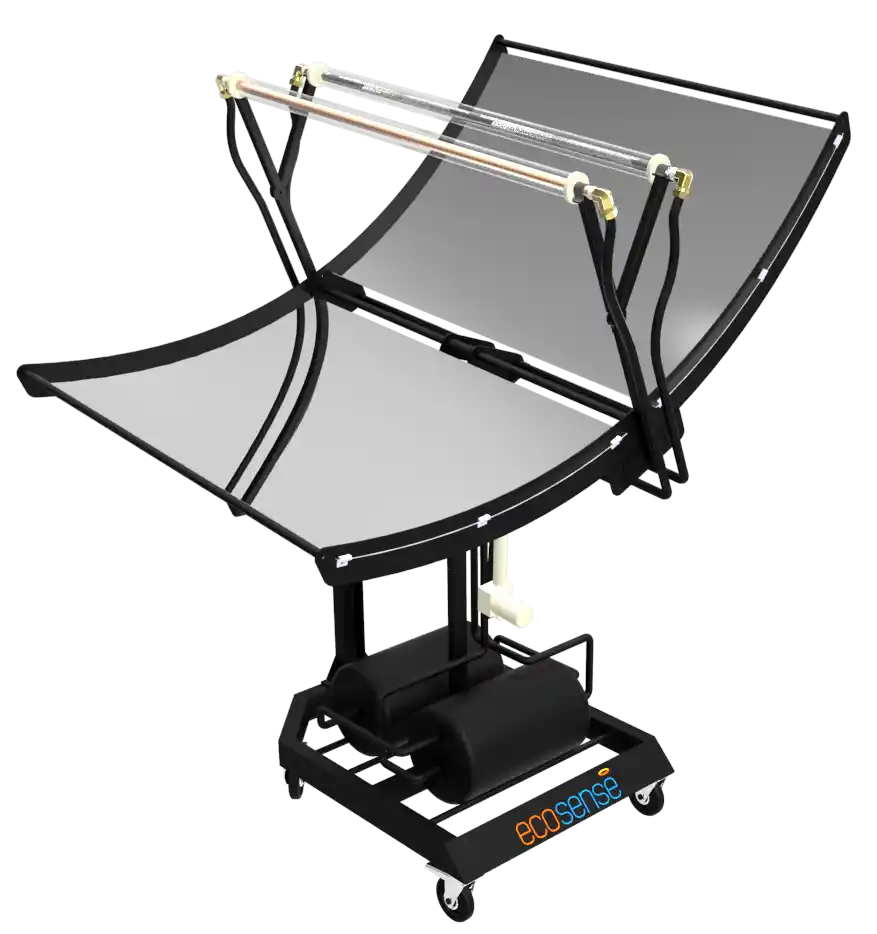
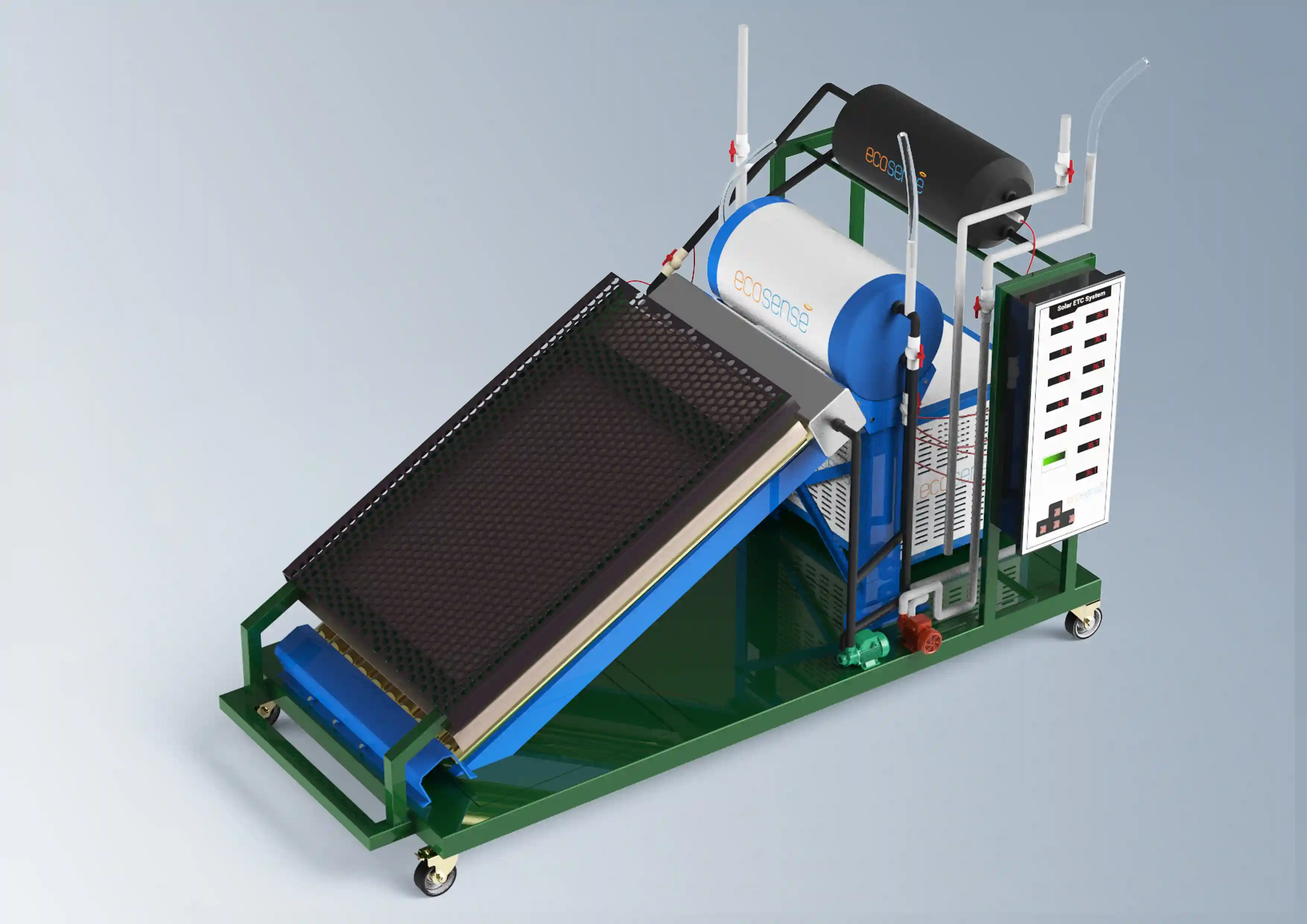
The Thermal Energy Storage System is a versatile experimental platform designed to facilitate in-depth studies of thermal energy storage using Phase Change Materials (PCMs). Engineered for both educational and research applications, this system enables users to explore the dynamics of heat transfer, storage, and retrieval under various operating conditions. Its modular design allows for experimentation with different PCMs, flow rates, and temperatures, making it an invaluable tool for understanding and optimizing thermal energy storage solutions.