Fuel Cell Drive Train
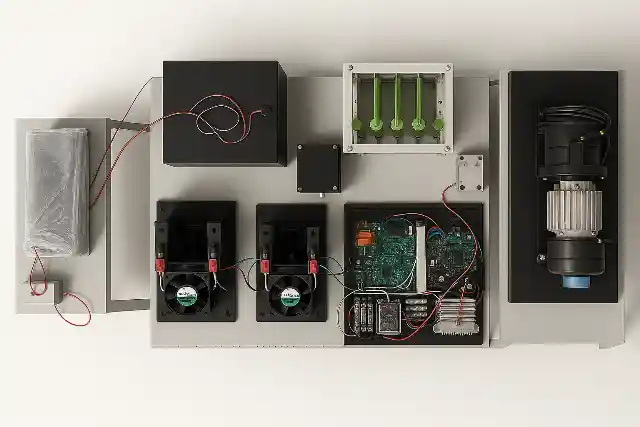
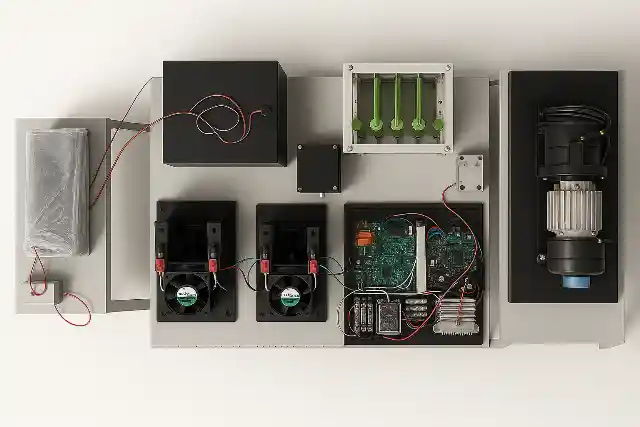
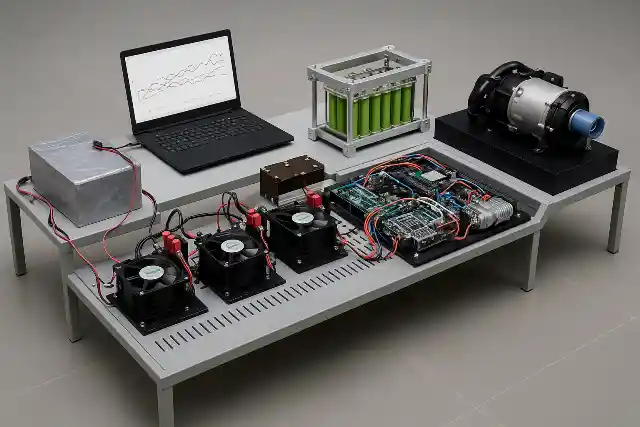
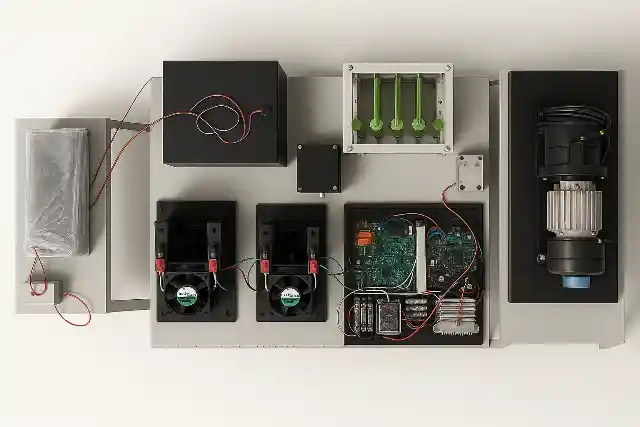
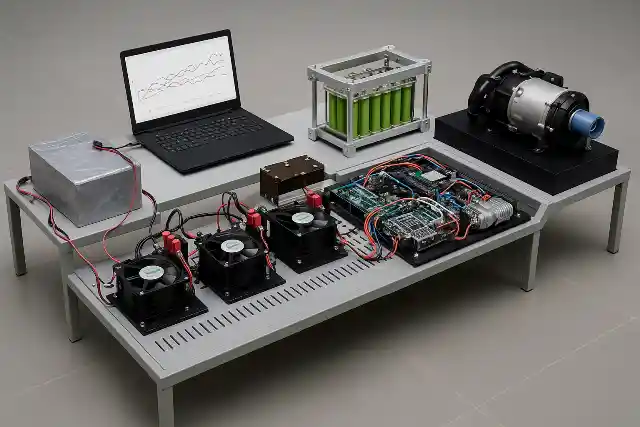
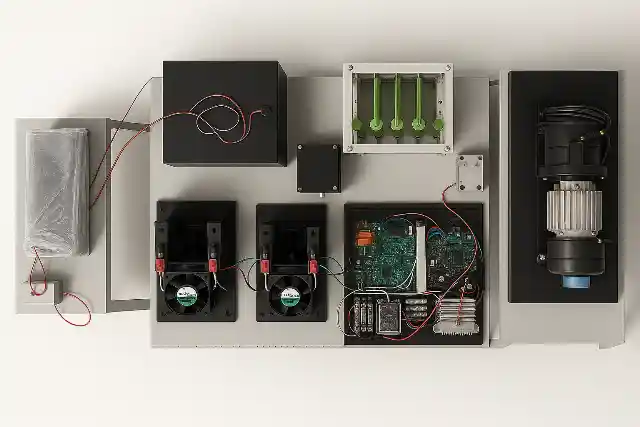
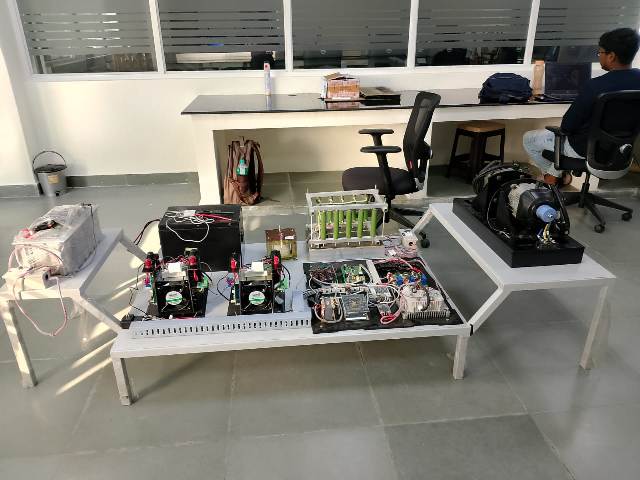
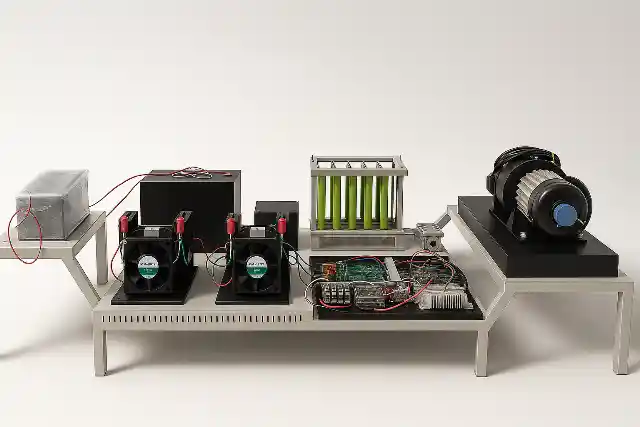
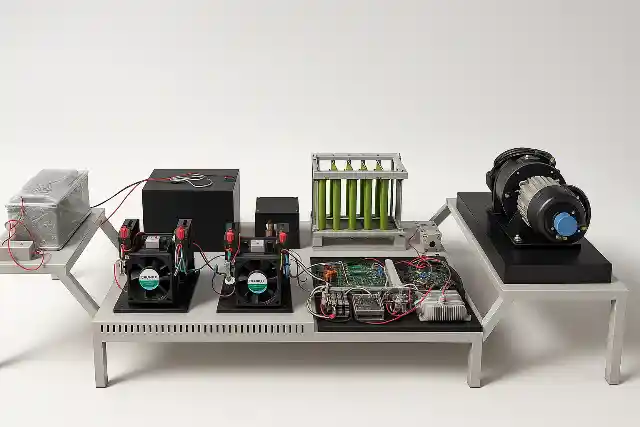
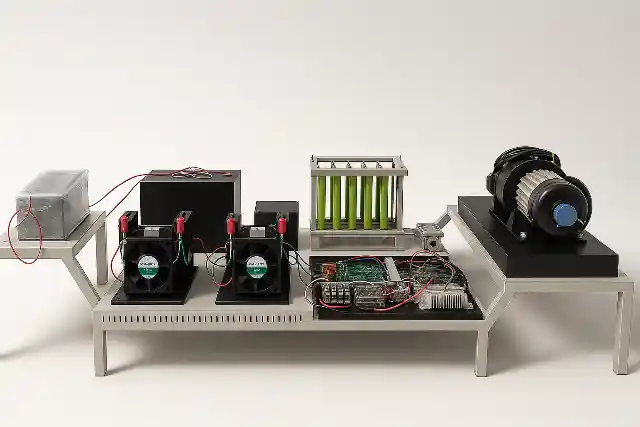
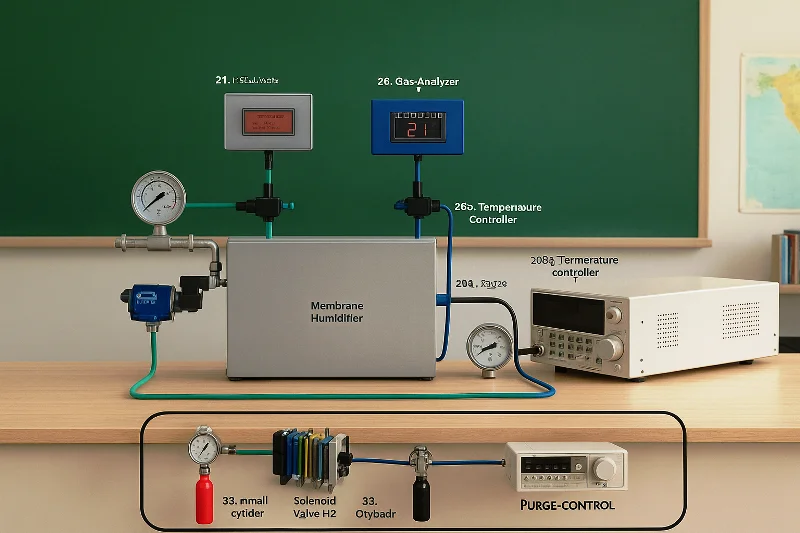
The Fuel Cell Drive Train is a modular laboratory platform designed to simulate and study the complete electric drive train of a hydrogen fuel cell hybrid electric vehicle (FCEV). It provides a hands-on learning environment that demonstrates how hydrogen energy is converted into electric propulsion through coordinated interaction between power electronics, energy storage systems, and motor drives. This lab-scale system integrates a PEM fuel cell, bidirectional power converters, battery bank, ultracapacitor module, and a complete motor drive setup. The traction system consists of a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) mechanically coupled to a PMDC loading motor and resistive load bank, enabling controlled road condition and load profile simulation. The architecture closely mirrors a real vehicle electric drive train, allowing detailed study of component-level and system-level behavior.